OpenWrt
Introduction
OpenWrt is an open source project for embedded operating system based on Linux, primarily used on embedded devices to route network traffic. All components have been optimized to be small enough to fit into the limited storage and memory available in home routers.
OpenWrt is configured using a command-line interface (ash shell), or a web interface (LuCI). OpenWrt can run on various types of devices, including CPE routers, residential gateways, smartphones, pocket computers and laptops etc.
Currently the OpenWrt can build
- AT91Bootstrap
- u-boot-at91
- linux-at91
- A cross-compiler optimized for at91 SoC
- Root filesystems of different types
- Bootable SD card Image
Related Links
How to build OpenWrt for AT91
Prerequisites
Host build system should be a Linux system with necessary software installed.
On Ubuntu/Debian you should also install libssl1.0-dev.
libssl provided by Ubuntu 20.04 doesn't fit with kernel necessities. The workaround for this is to do the following before installing libssl1.0-dev:
Edit /etc/apt/sources.list file and add the following line at the end:
Update:
 You can install missing packages using yum install with Fedora or apt-get install with Ubuntu or Debian. These commands may require root privileges or being in a correct sudoers group.
You can install missing packages using yum install with Fedora or apt-get install with Ubuntu or Debian. These commands may require root privileges or being in a correct sudoers group.
Get sources
You can easily download OpenWrt sources from our OpenWrt git repository.
To get the source code, you should clone the repository:
Cloning into 'openwrt-at91'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 44, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (44/44), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (37/37), done.
remote: Total 420102 (delta 17), reused 13 (delta 7), pack-reused 420058
Receiving objects: 100% (420102/420102), 148.16 MiB | 190.00 KiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (285014/285014), done.
$ cd openwrt-at91
$
The source code has been taken from the master branch which is pointing on the latest version of OpenWrt. If you want to use a specific release, you can list them and use one of them by doing this:
To benefit the latest enhancements for Microchip products, you are advised to use the openwrt-19.07.2-at91 branch.
Build OpenWrt images
Up to linux4sam-2021.11
The OpenWrt image contains the following components:
- BOOT.BIN (AT91Bootstrap)
- U-boot.bin (U-Boot)
- zImage (kernel image)
- at91 Device tree blob
- Root filesystems of different types
- Bootable SD card Image
The OpenWrt build system configuration interface handles the selection of the target platform, packages to be compiled, packages to be included in the firmware file, some kernel options, etc. Start the OpenWrt build system configuration interface by issuing the following command
Download and install all available "feeds" (see Openwrt feeds for more options):
for more options):
$ ./scripts/feeds install -a
NOTE: It is possible to create out of tree builds by setting the TOPDIR environment variable and creating the appropriate directory structure (see this for details). Otherwise make sure that TOPDIR is not set before running ./script/feeds, to avoid errors regarding missing files or directories.
for details). Otherwise make sure that TOPDIR is not set before running ./script/feeds, to avoid errors regarding missing files or directories.
You'll find a configs folder containing several default configurations for different At91 sama5 targets. If you want to build the OpenWrt image we provide for sama5d2_Xplained board, you'll have to do:
$ make defconfig
Everything is now ready for building the image(s), which is done with one single command:
After a successful build, the freshly built images can be found in the newly created at91 directory in <openwrt-at91>/bin/target/ directory. The compiled files are additionally classified by the target platform, so e.g. a firmware built for an at91 sama5d2 xplained device will be in <openwrt-at91>/bin/target/at91/sama5-glibc directory
at91bootstrap-sama5d2_xplaineddf_qspi_uboot
at91bootstrap-sama5d2_xplaineddf_uboot
at91bootstrap-sama5d2_xplainedsd_uboot
at91dtoverlay-sama5d2_xplained
config.buildinfo
feeds.buildinfo
openwrt-19.07.2-linux4sam-2021.04-at91-sama5-at91-sama5d2_xplained.dtb
openwrt-19.07.2-linux4sam-2021.04-at91-sama5-at91-sama5d2_xplained-ext4-root.ubi
openwrt-19.07.2-linux4sam-2021.04-at91-sama5-at91-sama5d2_xplained-ext4-sdcard.img.gz
openwrt-19.07.2-linux4sam-2021.04-at91-sama5-at91-sama5d2_xplained-ext4-zImage
openwrt-19.07.2-linux4sam-2021.04-at91-sama5-at91-sama5d2_xplained-ubifs-root.ubi
openwrt-19.07.2-linux4sam-2021.04-at91-sama5-at91-sama5d2_xplained-ubifs-zImage
openwrt-19.07.2-linux4sam-2021.04-at91-sama5-at91-sama5d2_xplained-uImage
openwrt-19.07.2-linux4sam-2021.04-at91-sama5-device-at91-sama5d2-xplained.manifest
openwrt-19.07.2-linux4sam-2021.04-at91-sama5-device-at91-sama5d2-xplained-rootfs.tar.gz
packages
sama5d2_xplained.itb
sha256sums
uboot.env
u-boot-sama5d2_xplained_mmc
u-boot-sama5d2_xplained_spiflash
version.buildinfo
To write the compressed image (*.img.gz) on the SD card, follow steps mentioned in Create a SD card with the demo.
Starting with linux4microchip-2022.04
Starting with linux4microchip-2022.04 there will be no images directly released by Microchip. OpenWrt support will be directly pushed to mainline OpenWrt and will rely on releases (starting with 22.02.x) provided by OpenWrt community .
Steps to compile mainline OpenWrt:
Download and install available "feeds" (see Openwrt feeds for more options):
$ ./scripts/feeds install -a
Prepare defconfig:
Select "Microchip (Atmel AT91)" as "Target System". Select proper Subtarget: SAM9X, SAMA5 or SAMA7. Select proper board at "Target Profile". Save config, exit and run make.
The output is still located in bin/target/at91/ directory.
Cross toolchain
While creating the OpenWrt images, OpenWrt will build a cross toolchain (or will download or use one present on your machine). You can find it under staging_dir/toolchain-arm_cortex-a5_gcc-8.4.0_glibc_eabi/bin
arm-openwrt-linux-addr2line arm-openwrt-linux-gcov-tool arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-gcov arm-openwrt-linux-gprof iconv
arm-openwrt-linux-ar arm-openwrt-linux-gdb arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-gcov-dump arm-openwrt-linux-ld ldd
arm-openwrt-linux-as arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-addr2line arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-gcov-tool arm-openwrt-linux-ld.bfd locale
arm-openwrt-linux-c++ arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-ar arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-gdb arm-openwrt-linux-nm localedef
arm-openwrt-linux-c++filt arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-as arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-gprof arm-openwrt-linux-objcopy makedb
arm-openwrt-linux-cpp arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-c++ arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-ld arm-openwrt-linux-objdump mtrace
arm-openwrt-linux-elfedit arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-c++filt arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-ld.bfd arm-openwrt-linux-ranlib pcprofiledump
arm-openwrt-linux-g++ arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-cpp arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-nm arm-openwrt-linux-readelf pldd
arm-openwrt-linux-gcc arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-elfedit arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-objcopy arm-openwrt-linux-size readelf
arm-openwrt-linux-gcc-8.4.0 arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-g++ arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-objdump arm-openwrt-linux-strings sotruss
arm-openwrt-linux-gcc-ar arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-gcc arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-ranlib arm-openwrt-linux-strip sprof
arm-openwrt-linux-gcc-nm arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-gcc-8.4.0 arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-readelf catchsegv tzselect
arm-openwrt-linux-gcc-ranlib arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-gcc-ar arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-size gencat xtrace
arm-openwrt-linux-gcov arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-gcc-nm arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-strings getconf
arm-openwrt-linux-gcov-dump arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-gcc-ranlib arm-openwrt-linux-gnueabi-strip getent
The build system configuration interface
The build system configuration interface handles the selection of the target platform, packages to be compiled, packages to be included in the firmware file, some kernel options, etc. Start the build system configuration interface by writing the following command:

Customizing Linux Kernel configuration
All the explanations are available in the OpenWrt developer guide under kernel configuration section.
Using an OpenWrt system
OpenWrt has the following ways to configure stuff:
- There is “UCI” (Unified Configuration Interface) to store and manipulate all its configuration. This is an OpenWrt-own format and standard for config files and command line utilities to configure OpenWrt-related stuff)
- There is “LuCi” - a web GUI interface for UCI, by default usually listening at http://192.168.1.1. LuCi is based on LUA and its a OpenWrt own standard as well. You can also enable https for LuCi access. Not all options may be available in LuCi and LuCi requires about 1MB of flash space.
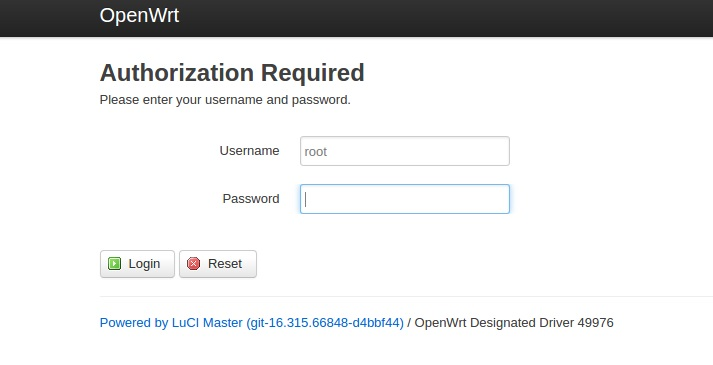
- There are several classic Linux config files also used in on OpenWrt devices. These files use the same format and config options as in other Linux distributions.
- Optional installable packages sometimes integrate into the UCI config model and may also provide a LuCi config extension, but many extension packages also bring their own config files* Root File System's
Related Topics